Heavy drinking puts you at greater risk for it but you can. Extensive scar tissue replaces healthy tissue.
 Severe Hepatic Steatosis Without Fibrosis 80 Steatosis On Histologic Download Scientific Diagram
Severe Hepatic Steatosis Without Fibrosis 80 Steatosis On Histologic Download Scientific Diagram
In imaging it can present in a typical homogeneous or heterogeneous way.

Severe hepatic steatosis. The diagnosis of hepatic steatosis is based on exclusion of other etiologies such as alcohol use. It is usually reversible once the cause of the problem is diagnosed and corrected. Scar tissue forms where your liver is damaged.
Hypertransaminasemia and severe hepatic steatosis without inflammation. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the Western world.
PDFF differentiated moderate or severe steatosis from mild or no steatosis with 930 sensitivity and 850 specificity. On imaging grounds it can broadly be divided into two groups. Steatosis or fatty liver is a common result of moderate to severe hepatocellular insult.
Also called steatosis fatty liver can be a temporary or long-term condition which is not harmful itself but may indicate some other type of problem. The terms hepatic steatosis and fatty liver disease. 1Department of Biomedical Research Medica Sur Clinic Foundation Mexico City Mexico.
In humans the most common cause of steatosis is insulin resistance associated with central obesity and sedentary life style non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic syndrome with alcohol-induced steatosis also a common occurrence Valenti et al 2013. Some forms create traps in imaging whether localised steatosis is concerned or areas which have been spared by steatosis and the purpose of this paper is to explain and illustrate them. Having small amounts of fat in your liver is normal but too.
Nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis also called liver steatosis hepatosteatosis or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD and describes the accumulation of fat in the liver that is not related to alcohol consumption. Steatosis of liver or Fatty Liver is a medical condition where large amounts of fats accumulate in the liver cells. Cirrhosis of the liver.
Hepatic steatosis refers to an increase of intracellular fat in the liver. It is projected to become a leading indication for liver transplantation superseding hepatitis C. It is an augmentation of fat in the hepatic cells and can cause complications in cases of obesity alcohol intoxication due to an excessive consumption of alcohol or hepatic disorders like diabetes Type 2.
Left untreated it can contribute to other illnesses. Hepatic steatosis is an accumulation of fat in the liver. Hepatic steatosis is a common condition the prevalence of which is increasing along with non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis.
2015 by the. Focal hepatic steatosis focal hepatic fat. Nonalcoholic Alcoholic Steatohepatitis NAFLDAFLD Fatty liver disease means you have extra fat in your liver.
Studies have indicated that over 70 obese people suffer from steatosis of liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. This stage is called steatohepatitis.
This process is called fibrosis. However the correlation between biopsy results and MR imaging was lower in patients with moderate or severe forms of hepatic steatosis compared with patients with more mild forms of steatosis. Your liver becomes inflamed swollen which damages its tissue.
Steatosis of liver usually occurs to those who drink excess alcohol and those who are obese. Fatty liver is also known as hepatic steatosis. Hepatic steatosis was classified by pathology as none S0 33 and quantitatively by controlled attenuation parameter CAP as CAP S0 247 dBm CAP S1 248-267 dBm and CAP S2-3 268 dBm.
It happens when fat builds up in the liver. Liver fibrosis was assessed by METAVIR classification and noninvasively by LSM. In patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease the presence of severe steatosis detected by histology or by US should always be taken into account in order to avoid overestimations of liver fibrosis assessed by transient elastography.
Complications may include cirrhosis liver cancer and esophageal varices. At this point you have cirrhosis of the liver. Méndez-Sánchez N1 Motola-Kuba D Bahena-Aponte J Chavez-Tapia N Pichardo-Bahena R Uribe M.
Fatty liver diseaseFLD also known as hepatic steatosis is a condition where excess fatbuilds up in the liver. It is widely mischaracterized by both radiologists and sonographers as fatty infiltration but the fat is in the hepatocytes and not in the extracellular matrix.
Hepatic Steatosis Sickness Finder
 Fatty Liver Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis
Fatty Liver Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis
 S3 Severe Steatosis Bright Liver With Intense Posterior Attenuation Download Scientific Diagram
S3 Severe Steatosis Bright Liver With Intense Posterior Attenuation Download Scientific Diagram
 Reduced Hepatobiliary Phase Enhancement Due To Severe Hepatic Steatosis Download Scientific Diagram
Reduced Hepatobiliary Phase Enhancement Due To Severe Hepatic Steatosis Download Scientific Diagram
 Hepatic Steatosis Fatty Liver Sonographic Tendencies
Hepatic Steatosis Fatty Liver Sonographic Tendencies
 Hepatic Steatosis A Major Trap In Liver Imaging Sciencedirect
Hepatic Steatosis A Major Trap In Liver Imaging Sciencedirect
 Liver Steatosis Is A Strong Predictor Of Mortality And Cancer In Chronic Hepatitis B Regardless Of Viral Load Sciencedirect
Liver Steatosis Is A Strong Predictor Of Mortality And Cancer In Chronic Hepatitis B Regardless Of Viral Load Sciencedirect
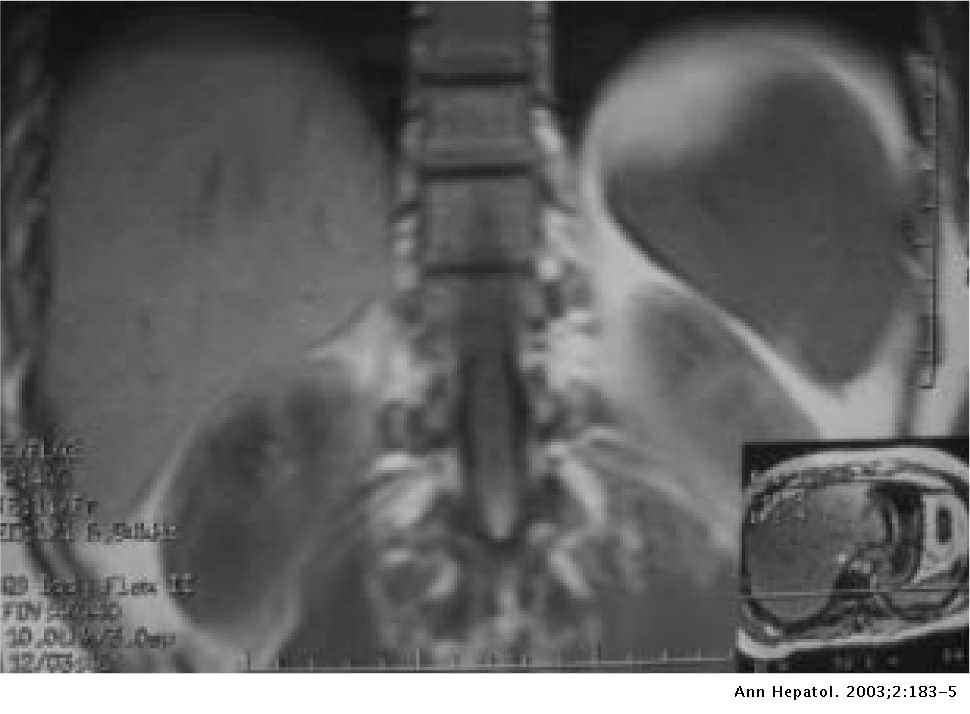 Hypertransaminasemia And Severe Hepatic Steatosis Without Inflammation A Case Report Annals Of Hepatology
Hypertransaminasemia And Severe Hepatic Steatosis Without Inflammation A Case Report Annals Of Hepatology
 Hepatic Steatosis And Its Effects On Fibrosis In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Clinical Gastroenterology And Hepatology
Hepatic Steatosis And Its Effects On Fibrosis In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Clinical Gastroenterology And Hepatology
 Ultrasound Findings In Hepatic Steatosis The Steatotic Liver Is Download Scientific Diagram
Ultrasound Findings In Hepatic Steatosis The Steatotic Liver Is Download Scientific Diagram
 Mri Evaluation Of Fatty Liver In Day To Day Practice Quantitative And Qualitative Methods Sciencedirect
Mri Evaluation Of Fatty Liver In Day To Day Practice Quantitative And Qualitative Methods Sciencedirect
 Automated Measurement Of Liver Attenuation To Identify Moderate To Severe Hepatic Steatosis From Chest Ct Scans European Journal Of Radiology
Automated Measurement Of Liver Attenuation To Identify Moderate To Severe Hepatic Steatosis From Chest Ct Scans European Journal Of Radiology
 Moderate Hepatic Steatosis Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Moderate Hepatic Steatosis Page 1 Line 17qq Com

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.