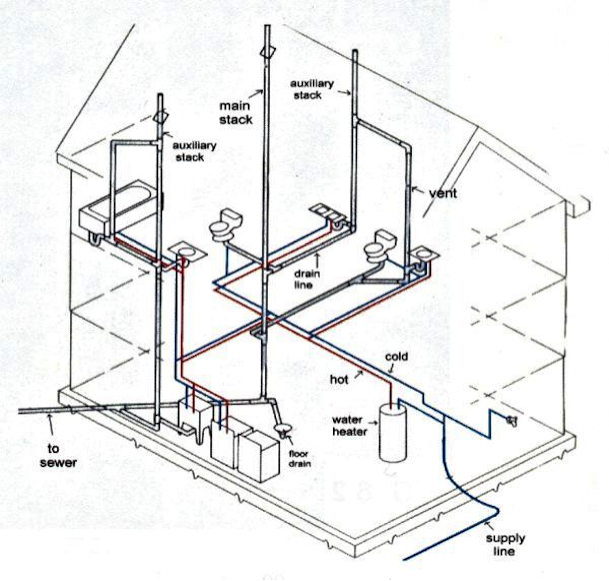
Thus vaccines prime our immune system to be better prepared for an infection if we are exposed to the pathogen again. How vaccines help Vaccines contain weakened or inactive parts of a particular organism antigen that triggers an immune response within the body.
 Vaccines Free Full Text Efforts At Covid 19 Vaccine Development Challenges And Successes Html
Vaccines Free Full Text Efforts At Covid 19 Vaccine Development Challenges And Successes Html
Viral vector vaccines use a safe virus to insert pathogen genes in the body to produce specific antigens such as surface proteins to stimulate an immune response.

Many vaccinations stimulate the immune system by exposing it to. If you wanted to gain immunity to measles by contracting the disease you would face a 1 in 500 chance of death from your symptoms. Vaccines work by preventing infections whereas antibiotics work by treating them. Prof Geraint Florida-James is the research lead for sport health and exercise sciences at Napier University in Edinburgh.
Vaccines typically contain part of a pathogen eg virus or bacterium and stimulate the production of antibodies against this pathogen. Still in experimental stages DNA vaccines would dispense with all unnecessary parts of a bacterium or virus and instead contain just an injection of a few parts of the pathogens DNA. But were still learning how vaccines will affect the spread of COVID-19.
After you are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 you may be able to start doing some things that you had stopped doing because of the pandemic. All vaccines work by priming the immune system against a potential infectious pathogen. These DNA strands would instruct the immune system to produce antigens for.
Vaccines work by exposing the body to a small part or weakened form of a particular virus so that the immune system can learn to recognise it and trigger the production of specific antibodies to fight off the infection. In this way the immune system can more easily recognize and destroy any of these microorganisms in future encounters. Assuming the quantities of antibodies likely generated by an individual in 1 ml of blood one-fifth of a teaspoon during seven days after exposure to a vaccine and the number of different specificities of those antibodies then each infant would have the capacity to.
An interesting 2012 paper Immunization with SARS Coronavirus Vaccines Leads to Pulmonary Immunopathology with Exposure to the Actual SARS Virus This paper demonstrates what many researchers now fear namely that COVID-19 vaccines may end up making people more prone to severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. It also primes immune cells to. Vaccines and antibiotics are two of the most powerful tools against bacterial infections.
A vaccine may weaken the immune system. While the live vaccines can provide lifelong immunity after only one or 2 doses periodic booster doses are needed to maintain immunity with some of the other types of vaccines. These elements of vaccines and other molecules and micro-organisms that stimulate the immune system are called antigens Babies are exposed to thousands of germs and other antigens in the environment from the time they are born.
Modern vaccines use various methods to stimulate immune response including inactivated or modified pathogens or fragments of the target pathogen. And toxoid vaccines which contain an inactivated bacterial toxin toxoid. Vaccines work with your immune system so your body will be ready to fight the virus if you are exposed.
Exposed to the antigens in the vaccine your immune cells start making antibodies and also produce long-lived memory T cells and memory B cells. If your immune system encounters the same antigen again the memory cells ensure that many specific antibodies. It stimulates the body to make antibodies against antigens of pathogens.
Vaccines contain weakened or killed versions of the germs that cause a disease. Modernas COVID-19 vaccine stimulates an immune response in people Early results suggest a coronavirus vaccine works but more human trials are. Subunit vaccines which contain just the part of the organism that stimulates an immune response the antigen.
The agent in a vaccine stimulates the bodys immune system to recognize the agent as foreign destroy it and remember it. Vaccination teaches the body to recognize new diseases. There are available vaccines against 23 diseases or pathogens that cause them.
Early vaccines used inoculation of a similar but harmless pathogen to develop immunity to deadly pathogens. This means that if the person is exposed to the dangerous pathogen in the future their immune system will be able to respond immediately protecting against disease. Antibiotics were first discovered in the early 1900s when a drug called sulfanilamide was found to protect people from fatal bacterial infections such as pneumococcus.
Vaccines stimulate the immune system to produce an immune response similar to natural infection It does not weaken or overload the immune system in any way.