In bone marrow biopsies stromal structural fibres are detected by reticulin and trichrome stains routine stains performed on bone marrow biopsy specimens in diagnostic laboratories. Bone Marrow Fibrosis and Early Hematological Response as Predictors of Poor Outcome in Azacitidine Treated High Risk-Patients With Myelodysplastic Syndromes or Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
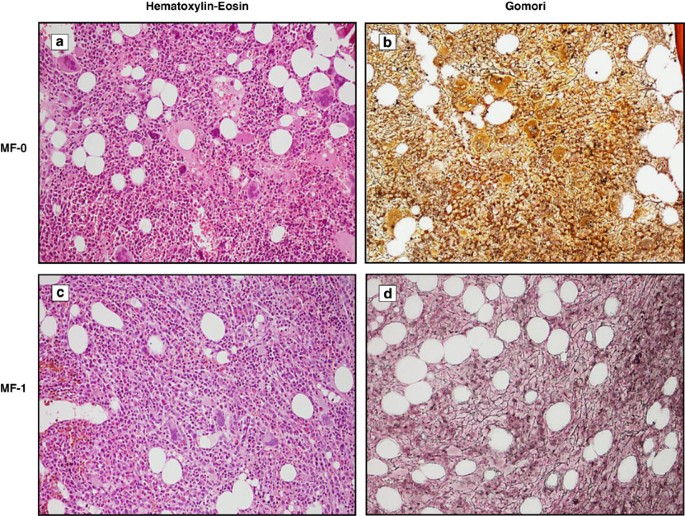 The European Consensus On Grading Of Bone Marrow Fibrosis Allows A Better Prognostication Of Patients With Primary Myelofibrosis Modern Pathology
The European Consensus On Grading Of Bone Marrow Fibrosis Allows A Better Prognostication Of Patients With Primary Myelofibrosis Modern Pathology
Although bone marrow fibrosis is seen in a variety of malignant and non-malignant disease states the deposition of reticulin and collagen fibrosis in the bone marrow of patients with myelofibrosis is believed.
Bone marrow fibrosis. Although bone marrow fibrosis is seen in a variety of malignant and non-malignant disease states the deposition of reticulin and collagen fibrosis in. Bone marrow fibrosis is a central pathological feature and World Health Organization major diagnostic criterion of myelofibrosis. It is a secondary change associated with such disorders as inflammation bone marrow necrosis bone marrow injury and disorders of myeloproliferation eg acute myeloid leukemia and.
You can think of the bone marrow niche as a comfortable bed with a soft mattress covered by blankets and pillows. Increased reticulin staining reticulin fibrosis is associated with many benign and malignant conditions while increased trichrome staining collagen fibrosis is particularly prominent in late stages of severe myeloproliferative diseases or following tumour metastasis to the bone marrow. Bone marrow fibrosis evaluated as reticulin fiber density RFD in bone marrow sections was evaluated at diagnosis via computer technology.
In a recent article by Campbell et al 1 published in Journal of Clinical Oncology a significant association between the degree of bone marrow BM fibrosis at diagnosis and progression of disease as well as risk of arterial thrombosis was found in patients with essential thrombocythemia ET. Pathophysiology and clinical significance of increased bone marrow stromal fibres. The most severe form is dyskeratosis congenita see eg 127750 characterized by early childhood onset of skin abnormalities bone marrow failure predisposition to malignancy and risk of pulmonary and hepatic fibrosisAdult-onset pulmonary fibrosis is the most common.
Bone marrow biopsy specimens in diagnostic laboratories. In non-technical terms it is a condition in which the place where blood cell precursors live becomes unfriendly. Im often asked to explain what exactly is bone marrow fibrosis.
Bone Marrow Fibrosis BMF a common morphological finding in trephine biopsies is observed with variable grades of severity in various lesions including primary as well as secondary myelofibrosis1 The study of pattern and extent of bone marrow Fibrous Tissue Content FTC is important not only in diagnosis but also in evaluation of prognosis2. In narrative descriptions of bone marrow fibrosis the term fibrosis should always be specified as either reticulin fibrosis or collagen fibrosis with the term collagen fibrosis being reserved for collagen identifiable by trichrome stain. Bone marrow fibrosis is a lesion characterized by an increase of reticulin fibers or reticulin and collagen fibers andor proliferating fibroblasts.
2012 Farlex Inc. Shortened telomeres can cause a wide variety of clinical features that constitute a phenotypic spectrum. An increase in fibres and in new bone results in disorganization of the bone marrow architecture dysplasia of the haematopoietic cell lines fibrosis of vessel walls and thereby impeded egress of mature cells from the bone marrow resulting in ineffective haematopoiesis peripheral cytopenia often the indication for the biopsy and possibly myeloid metaplasia which has been found in many.
A general term for the presence of increased reticulin in the bone marrow which causes spindling of the marrow cells. Receiver operating characteristic curve ROC was used to analyze the predictive value of RFD for relapse and survival status. Bone marrow BM is traditionally called bone marrow fibrosis or myelofibrosis MF 9.
It shows a step-wise evolution from a physiologically normal state through first minimal focal and latter on diffuse increase of reticulin fibers up to the formation of collagenous fibers in advanced stages of the process associated in some of the. Reda G Riva M Fattizzo B Cassin R Giannarelli D Pennisi M Freyrie A Cairoli R Molteni A Cortelezzi A Semin Hematol 2018 Oct554202-208. Bone marrow fibrosis is a common phenomenon and is observed in various pathological conditions such as myeloproliferative and myelodysplastic neoplasms leukemias lymphomas mastocytosis paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria plasma cell myeloma Gauchers disease granulomas metastatic tumors hyperparathyroidism chronic renal failure osteopetrosis autoimmune disorders and Pagets disease.
Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate survival rates per subgroup. Systemic mastocytosis cancer carcinoma lymphoma myeloma myeloproliferative disorders HIV. Grading scales for the.
Bone marrow fibrosis is a central pathological feature and World Health Organization major diagnostic criterion of myelofibrosis.
