This occurred in Spain with a 4 year old boy presented with a history of needlestick injury involving a needle from a. PEP should be used only in emergency situations.
 What Should You Do If You Get A Needlestick The Hospitalist
What Should You Do If You Get A Needlestick The Hospitalist
Healthcare personnel who use or may be exposed to needles are at increased risk of needlestick injury.

Hiv needlestick risk. Wash needlesticks and cuts with soap and water. If you experienced a needlestick or sharps injury or were exposed to the blood or other body fluid of a patient during the course of your work immediately follow these steps. 023 1 in 435 Blood transfusion with contaminated blood.
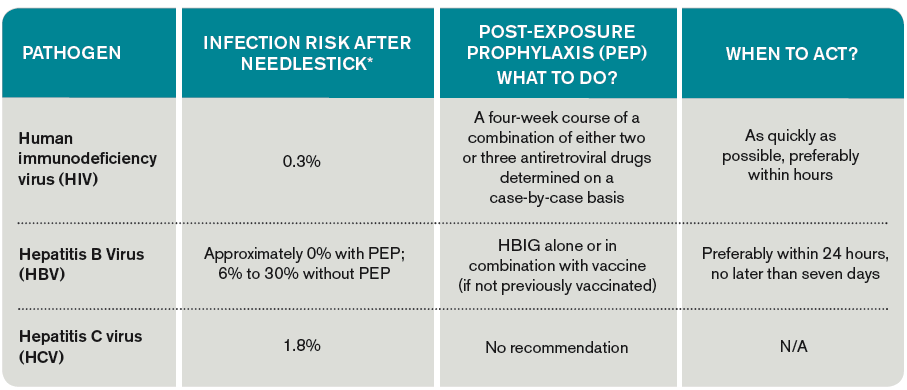
PEP must be started within 72 hours 3 days after a possible exposure to HIV. HIV The average risk of HIV infection after a needlestick or cut exposure to HlV-infected blood is 03 ie three-tenths of one percent or about 1 in 300. Post-exposure prophylaxis PEP means taking HIV medicines within 72 hours after a possible exposure to HIV to prevent HIV infection.
Hepatitis B virus HBV hepatitis C virus HCV human immunodeficiency virus HIV. 17 rows HIV Risk Behaviors. PEP is safe but the HIV medicines used for PEP may cause side effects like nausea in some people.
However other infectious agents also have the potential for transmission through needlestick injury. 063 1 in 158 Needlestick injury with contaminated blood. 925 9 in 10 A key factor determining the risk of transmission is the amount of virus in body fluids which is known as viral load.
Irrigate eyes with clean water saline or sterile irrigants. The risk of getting HIV varies widely depending. The risk of seroconversion following needlestick injury may be reduced by knowledge of body fluids that are high risk and knowledge of post-exposure prophylaxis following possible HIV-contaminated needlestick injury.
It is not meant for regular use by people who may be exposed to HIV frequently. The risk after exposure of the eye nose or mouth to HIV-infected. PEP must be started as soon as possible to be effectiveand always within 72 hours of a possible exposure.
The results suggest that perceived risk of HIV infection via needlestick ultimately influences follow-up medical screening. PEP is the use of antiretroviral drugs after a single high-risk event to stop HIV seroconversion. Approximately 03 risk of seroconversion after needle stick injury.
Greater concern about HIV is significantly associated with HIV screening and willingness to obtain post-exposure prophylaxis. Stated another way 997 of needlestickcut exposures do not lead to infection. HIV Needle Stick Risk Assessment Stratification Protocol RASP Quantifies HIV exposure risk by source and exposure type and need for prophylaxis.
The major blood-borne pathogens of concern associated with needlestick injury are. Path to Improved Health. Basic PEP QAs learn the basics about PEP and if its right for you.
Learn more about how to protect yourself and your coworkers from needlestick injuries. If you are taking PEP talk to your health care provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or. Flush splashes to the nose mouth or skin with water.
Needlestick injuries can lead to serious or fatal infections with bloodborne pathogens such as hepatitis B virus hepatitis C virus or HIV. The risk of exposure from direct skin contact with the fluid is less than 01. In almost all cases these side effects can be treated and arent life-threatening.
The risk of getting HIV from a needlestick injury is less than 1. The risk of infection from a human bite is between 01 and 1. However Kermode 2003 states that there has been one documented case of probable bloodborne virus transmission due to a needlestick injury that of HBV.
