Hindricks G Potpara T Dagres N et. 3 This is likely to be an underestimation because silent atrial fibrillation asymptomatic subclinical has not been taken into account.
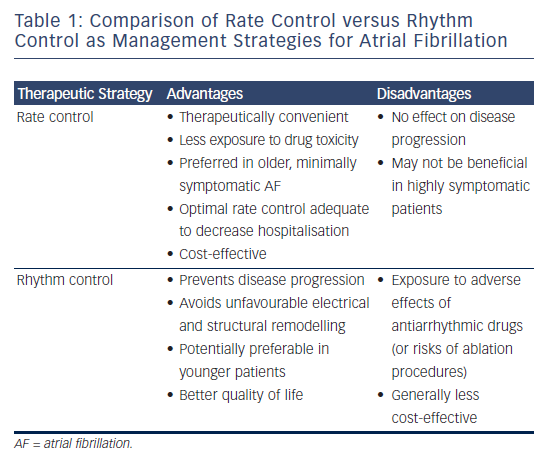
 Factors Favouring Rate Versus Rhythm Control Download Table
Factors Favouring Rate Versus Rhythm Control Download Table
But it is possible for the heart rate to be within accepted limits or slower and still be in atrial fibrillation.
Atrial fibrillation rate. When the fibrillary waves are more than 1 mm in amplitude they can be considered as coarse atrial fibrillation. A Fib Atrial fibrillation AF is the most common cardiac arrhythmia Prevalence increases with age - 1 in 5 people over the age of 85 years having the condition compared to. Suddenly starts and terminates spontaneously or with intervention within 7 days respond well to rate control alone typically with a beta-blocker such.
Rapid ventricular rates may result in degeneration to VT or VF. The American Heart Association explains your risk for atrial fibrillation or afib the symptoms of atrial fibrillation or afib diagnosis of atrial fibrillation or afib treatment of atrial fibrillation or afib and much more. AF with a controlled ventricular response mean heart rate 95 beats per minute bpm.
Substantial research efforts and resources are being directed towards gaining detailed information about the mechanisms underlying AF its natural course and effective treatments. The choice of rate control depends on the symptoms and clinical characteristics of the patient but for all patients with atrial fibrillation rate control is part of the management. New evidence is continuously generated and published.
Learn about symptoms and risk factors. Symptomatic tachycardia and stroke risk are the major issues seen in patients with atrial fibrillation. Fine fibrillary waves are seen throughout the baseline indicating fine atrial fibrillation.
The prevalence of atrial fibrillation in Australia is 24 with a predominance in older people. Atrial fibrillation often called AFib or AF is the most common type of treated heart arrhythmia. When a person has AFib the normal beating in the upper chambers of the heart the two atria is irregular and blood doesnt flow as well as it should from the.
Coarse atrial fibrillation usually indicates larger re-entrant circuits and hence. AF reverting to sinus bradycardia after a long reversion pause. Atrial flutter is a type of abnormal heart rate.
Most commonly the heart rate will be unusually fast with this condition. It occurs when the upper chambers of your heart beat too fast. Atrial fibrillation AF is a rhythm disturbance of the atria that results in irregular chaotic ventricular waveforms varying from bradyarrhythmia to tachyarrhythmia.
Atrial fibrillation AF poses a significant burden to patients physicians and healthcare systems globally. High rate of procedural success and low rates of procedure-related complications consistent with post-approval rates 12 14 15 CAP 1CAP2 NESTed SAP2 Major Procedural Complications defined as death ischemic stroke systemic embolism or deviceprocedure-related events necessitating cardiac. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology ESC Developed With the Special.
ECG features of Atrial Fibrillation in WPW are. Most patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ie. Essentially all forms of AF therapy can be divided into two categories - restoration and maintenance of normal sinus rhythm or control of the ventricular rate while permitting on-going fibrillation of the atria.
Control in patients with atrial fibrillation including the rationale for the intervention patient selection and the treatments available. Common patterns of ventricular rates in atrial fibrillation AF A. The rate of impulses in the atria can range from 300 to 600 beats per minute.
AF with a slow ventricular response mean heart rate 36 bpm. Atrial fibrillation AF is a condition that causes an irregular heart rate. Rate 200 bpm.
Atrial fibrillation AF with slow ventricular rate. Most atrial fibrillation in Australia is nonvalvular. Atrial fibrillation can occur in up to 20 of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome WPW The accessory pathway allows for rapid conduction directly to the ventricles bypassing the AV node.
Leads V4 and V5 of an electrocardiogram showing atrial fibrillation with somewhat irregular intervals between heart beats no P waves and a heart rate of about 150 beats per minute. Paroxysmal is intermittent meaning it comes and goes and continuous is persistent. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration With the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery EACTS.
Rate control in most cases of atrial fibrillation is the preferred approach to therapy. An arrhythmia is when the heart beats too slowly too fast or in an irregular way. Atrial fibrillation also called afib or af is a quivering heartbeat or irregular heartbeat that can lead to stroke and other heart-related complications.
None heart palpitations fainting shortness of breath chest pain. You can measure your heart rate by feeling the pulse in your wrist or neck. There are two types of atrial fibrillation.
The ventricles contract irregularly leading to a rapid and irregular heartbeat. AF with an uncontrolled or fast ventricular response mean heart rate 115 bpm and left bundle branch block aberrancy.
