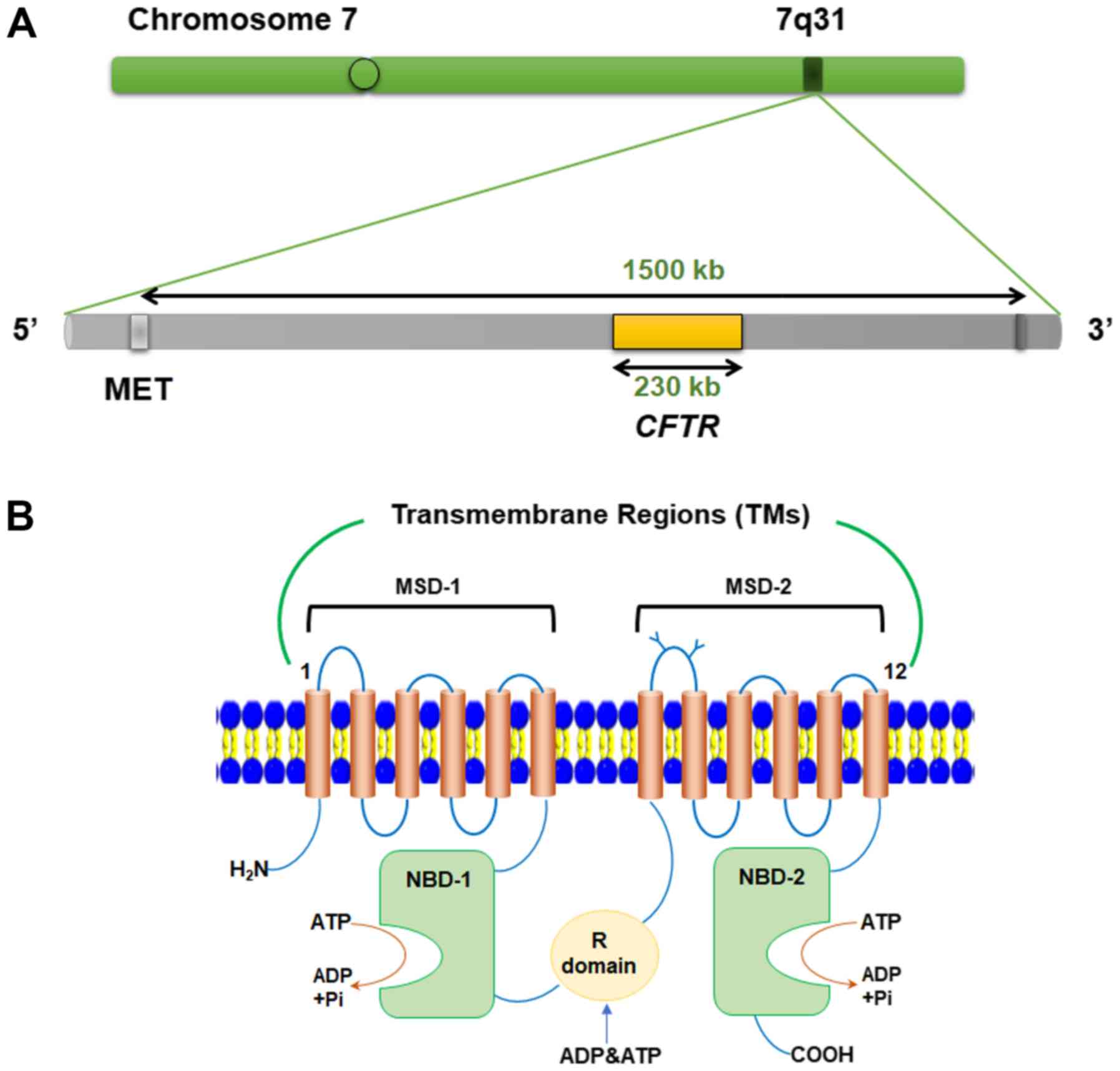
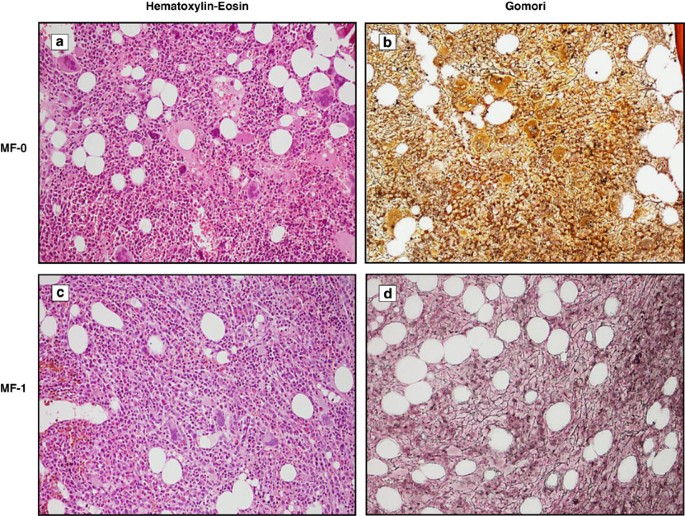
Liver fibrosis is scar tissue in the liver created when the liver tries to repair an injury. Fibrosis develops when the liver is repeatedly or continuously damaged.
 Diagnosing Liver Fibrosis Choosing The Right Test For You
Diagnosing Liver Fibrosis Choosing The Right Test For You
Liver fibrosis does not cause signs or symptoms.
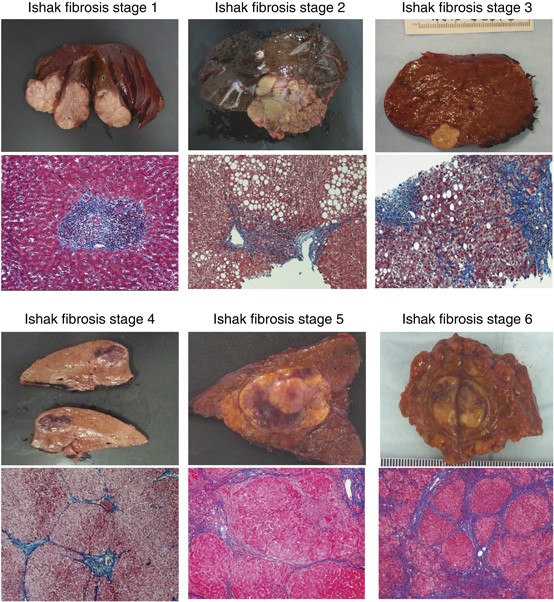
Stage 4 liver fibrosis. Liver fibrosis occurs when chronic injury or inflammation causes a buildup of scar tissue. This interferes with the livers ability to function and regenerate. Fibrosis stage 3 can be deemed serious if there is a high chance you will progress to stage 4 and then cirrhosis which may cause permanent damage to the liver.
If fibrosis is left untreated it can lead to cirrhosis and liver. What is Stage 4 Fibrosis of the Liver. Board-certified doctor now wait time is less than 1 minute.
This fibrosis 4 FIB4 score calculator reveals whether there is significant liver fibrosis of different stages associated to cirrhosis using patient age AST ALT. Fibrosis occurs as a result of an exaggerated response of the liver to chronic aggressions that regardless of their origin cause tissue damage. Talk to a doctor now.
The term cirrhosis is reserved for stage 4. After a single episode of injury even if severe as with acute hepatitis the liver commonly repairs itself by making new liver cells and attaching them to the web of connective tissue internal structure that is left when liver cells dieHowever if injury is repeated or continuous as occurs in chronic hepatitis. Stage 4 Liver Fibrosis.
Advanced fibrosis traditionally refers to stages 3 and 4. As cirrhosis progresses there will be an increased production of scar tissue making it difficult for the liver to function ultimately ending up in liver. Fibrosis in mild to moderate stages often does not cause symptoms.
Stage 4 liver cirrhosis presents the same symptoms as stage 3 with the addition of intensified confusion hand tremors high fever changes in personality infection in the abdominal cavity. Severe scarring of the tissues which leads to Liver cirrhosis or absolute blockage. Symptoms of Liver Fibrosis The major problem with the disease is that in early stages of liver fibrosis there are no noticeable symptoms and liver mostly functions absolutely normally helping to lead a usual and active life.
Cirrhosis is the end stage of fibrosis in the liver which is caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions like hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. It also removes harmful material from your body such as alcohol and other chemicals. You can read more about the Fibrosis 4 index its components and formula and about liver fibrosis below the form.
What can be done for stage 4 hepatic fibrosis Connect by text or video with a US. Due to a lack of symptoms many people live with liver damage or fibrosis without being diagnosed until they have symptoms of cirrhosis. Our study compared liver disease progression and survival in patients with stage 3 F3 and stage 4 F4 fibrosis on liver biopsy.
Common fibrosis terminology Fibrosis stage 2 is considered significant fibrosis. The liver makes enzymes and bile that help digest food and gives your body energy. Stage 3 should be taken very much as a warning signal that the liver is inflamed however you have time and a chance to reduce disease progression by drug therapy or by undertaking lifestyle changes depending on the type of liver.
It is the final common route in the evolution of multiple liver pathologies whose last stage is cirrhosis. The scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue over time. Advanced liver fibrosis is an important predictor of liver disease progression and mortality and current guidelines recommend screening for complications of cirrhosis once patients develop F3 fibrosis.
Fibrosis can be reversed if detected early enough and the underlying liver disease that caused the development of fibrosis can be cured or treated.