Although the high incidence 0330 and mortality rate 16931 of PE in patients undergoing major surgical procedures is apparent from findings of contemporary observational studies there is a lack of a summary and meta-analysis data on the epidemiology of postoperative PE in this same regard. Patients with acute pulmonary embolism who develop acute pulmonary hypertension greater than 50 mmHg that does not resolve in the first few weeks are at highest risk for progression particularly if the event is recurrent pulmonary embolism.
 Time Trends In Pulmonary Embolism Mortality Rates In The United States 1999 To 2018 Journal Of The American Heart Association
Time Trends In Pulmonary Embolism Mortality Rates In The United States 1999 To 2018 Journal Of The American Heart Association
Pulmonary infarction or death of a part of the lung.

Pulmonary embolism death rate. There were 2300 deaths from the condition in 2012. According to the AHA the study found that death rates for PE had dropped an average of 44 per year from 1999 to 2008 then began climbing an average of 06 per year. 98219 and 451 95.
Mortality of patients with pulmonary embolism. It is dangerous because almost a quarter of pulmonary embolism cases present as sudden death and up to a third of pulmonary embolism will ultimately be fatal. This decline slowed after 2006 across age groups and sexes.
The survival rate of a pulmonary embolism increases with early detection and proper treatment which is actually based on the stable size of clotting. Most patients 603 were treated with anticoagulants alone. For example it may cause a sudden collapse.
Abnormal rhythms of the heartbeat. Overall the incidence and mortality rate of COVID-19 patients developing PE was 153 95. While historically annual deaths from PE have been estimated to be 100 000 this number was extrapolated using the incidence of PE and applying historical case fatality rates rather than using measured deaths.
The biggest increases were for patients age 65 years. The incidence of death due to recurrent pulmonary embolism or significantly debilitating or. Its common with almost a million cases a year in the US alone.
The overall age-standardised annual mortality rate was 51 deaths per 100 000 population with 49 deaths per 100 000 women versus 53 per 100 000 men. Pulmonary Embolism A Big Deal Pulmonary embolism is a big deal being both common and dangerous. The proportion of male patients admitted with PE increased from 449 in 1993 to 473 in 2012.
Among patients in the highest-risk groups the 7-day mortality ranged from 70 18 patients to 163 7 patients whereas 30-day mortality. 920 p 0001 and mortality I2. 207 men 498 7-day mortality in the low-risk groups ranged from 13 1 patient to 31 4 patients whereas 30-day mortality ranged from 26 1 patient to 102 13 patients.
Some evidence of statistical heterogeneity among the studies reporting PE incidence I2. Pulmonary embolism PE is a life-threatening condition common after major surgery. The complications that pulmonary embolism gives rise to Shock.
The rate of recurrent thromboembolism is less than 5. From 1999 to 2017 there were 58784 patients in United States with a primary diagnosis of PE that was defined as high-risk. How many people died from pulmonary embolism 2008 - 2012 Between 2008 and 2012 the number of people who died from pulmonary embolism went down by 30.
The death rate after pulmonary embolism is less than 5 during 3-6 months of anticoagulant treatment provided that the patient is hemodynamically stable and free of major underlying disease. In Canada the annual age-standardised mortality rate from PE as the underlying cause of death decreased from 47 deaths per 100000 population 4450 in 2000 to 26 deaths per 100000 population 2428 in 2017. 4 Our study uses direct measures of mortality and the data are consistent with estimates of annual PErelated mortality for 2017 published by the American Heart Association.
Patients being risk-assessed for the condition when admitted to. However patients stable enough for diagnostic procedures as Spiral CTs and VQ-Scans had mortality rates of 1 to 2. Patients with PE who received mechanical ventilation cardiopulmonary resuscitation and thrombolytic treatment had very high mortality rates of 80 77 and 30 respectively.
786 p 0001 in COVID-19 was observed Fig. Because of the blood clot the function of the heart can stop suddenly which can cause the sudden cardiac arrest or death. With this definition the crude annual pulmonary embolism-related mortality rate was 45 deaths per 100 000 population in the WHO European Region.
Pleural effusion or a build-up of fluid developing between the outer lining of the lungs and the inner linings of the chest cavity. Mortality in 1999 was 727 decreasing to 498 in 2017 P. Results Among 416 patients with acute pulmonary embolism mean SD age 613 176 years.
The rate of both massive PE and mortality increased 15 to 28 per 100000 and 16 to 21 per 100000 respectively but not commensurate with the increase in admissions.
 Crude Mortality Rates From Pulmonary Embolism By Age Group And Gender Download Scientific Diagram
Crude Mortality Rates From Pulmonary Embolism By Age Group And Gender Download Scientific Diagram
 Total Number Of Pulmonary Embolism Deaths By Age Group For Men A Download Scientific Diagram
Total Number Of Pulmonary Embolism Deaths By Age Group For Men A Download Scientific Diagram
Pulmonary Embolism Mortality In Brazil From 1989 To 2010 Gender And Regional Disparities
 Hospital Volume And Outcomes For Acute Pulmonary Embolism Multinational Population Based Cohort Study The Bmj
Hospital Volume And Outcomes For Acute Pulmonary Embolism Multinational Population Based Cohort Study The Bmj
 Crude Mortality Rates From Pulmonary Embolism By Age Group Download Scientific Diagram
Crude Mortality Rates From Pulmonary Embolism By Age Group Download Scientific Diagram
 2019 Esc Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management Of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Developed In Collaboration With The European Respiratory Society Ers European Respiratory Society
2019 Esc Guidelines For The Diagnosis And Management Of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Developed In Collaboration With The European Respiratory Society Ers European Respiratory Society
 World Thrombosis Day Pulmonary Embolism
World Thrombosis Day Pulmonary Embolism
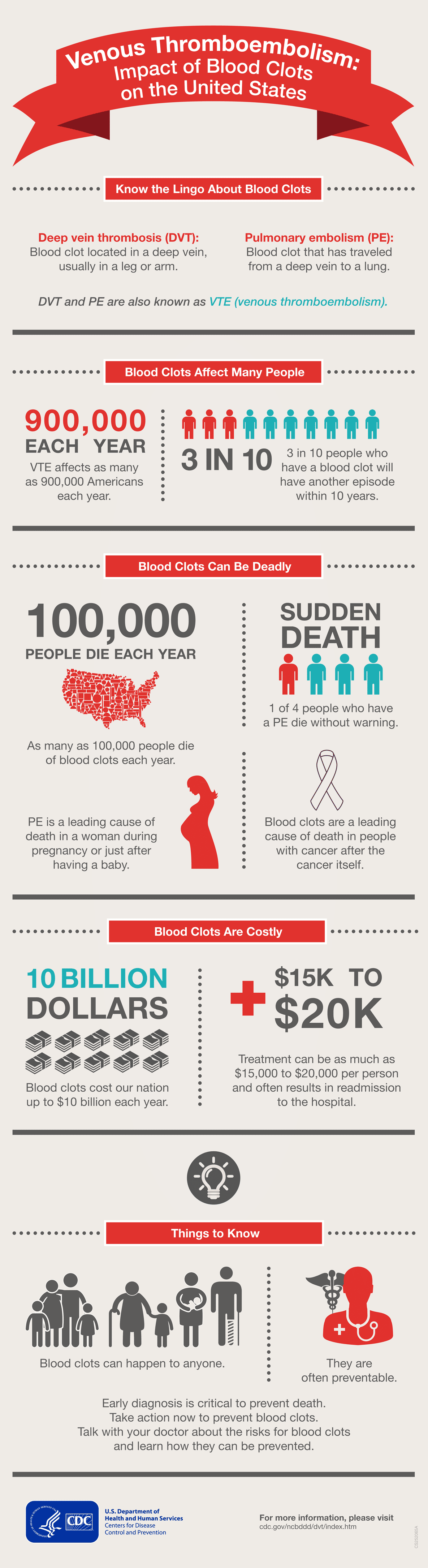 Impact Of Blood Clots On The United States Cdc
Impact Of Blood Clots On The United States Cdc
 Age Sex Specific Pulmonary Embolism Related Mortality In The Usa And Canada 2000 18 An Analysis Of The Who Mortality Database And Of The Cdc Multiple Cause Of Death Database The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Age Sex Specific Pulmonary Embolism Related Mortality In The Usa And Canada 2000 18 An Analysis Of The Who Mortality Database And Of The Cdc Multiple Cause Of Death Database The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
 Relative Mortality Rate Of Pulmonary Embolism In Patients With And Download Scientific Diagram
Relative Mortality Rate Of Pulmonary Embolism In Patients With And Download Scientific Diagram
 Classification Of Patients With Acute Pe Based On Early Mortality Risk Download Table
Classification Of Patients With Acute Pe Based On Early Mortality Risk Download Table
 Acute Pulmonary Embolism Mortality Prediction By The 2014 European Society Of Cardiology Risk Stratification Model European Respiratory Society
Acute Pulmonary Embolism Mortality Prediction By The 2014 European Society Of Cardiology Risk Stratification Model European Respiratory Society
 Crude Mortality Rates From Pulmonary Embolism By Gender And Ages And Download Scientific Diagram
Crude Mortality Rates From Pulmonary Embolism By Gender And Ages And Download Scientific Diagram
 Figure 1 From Case Fatality Rate In Pulmonary Embolism According To Age And Stability Semantic Scholar
Figure 1 From Case Fatality Rate In Pulmonary Embolism According To Age And Stability Semantic Scholar

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.