Chronic renal disease CRD happens when a condition or a disease impairs the kidney function resulting in damage to kidney that it worsened in months or few years. Discusses significant advances in the fieldincluding those related to pathophysiology of glomerular diseases electrolyte disorders renal tubular transport systems hypertension transplantation hereditary diseases and chronic kidney diseaseto keep your knowledge current.
 Pathophysiology Of Acute Kidney Injury Aki And Hepatorenal Syndrome Download Scientific Diagram
Pathophysiology Of Acute Kidney Injury Aki And Hepatorenal Syndrome Download Scientific Diagram
The tips or papilla of the renal pyramids projects into a funnel shaped chamber called a minor calyxThe minor calyces join up to form the renal pelvis.
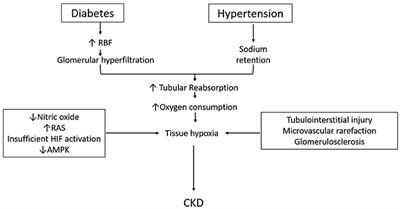
Pathophysiology of kidney. GFR 60 mLmin173m 2 for 3 months with or without kidney damage-Pathological abnormalities on kidney biopsy or Guidelines 2002 NKFKDOQI. Inability to remove potassium from the bloodstream may lead to abnormal heart rhythms and sudden death. Abnormalities of the kidney with ou without decreased GFR manifest by either -Markers of kidney damage such as proteinuria abnormal urinary sediment or abnormalities in imaging tests 2.
Chronic Renal Disease CRD is known as chronic renal insufficiency or chronic renal failure. Asymptomatic more susceptible to develop azotemia II renal insufficiency. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood which are then excreted in your urine.
AKI among hospitalized patients is associated with increased length of stay and. Edema hypocalcemia metabolic acidosis. Pathophysiology of the kidneys The kidneys are paired organs 11-14 cm in length in adults 5-6 cm in width and 3-4 cm in depth.
The major limitation to such data is its correlative nature and unsuitability for precise hypothesis testing. Often the first sign of kidney disease from diabetes is protein in your urine. A healthy kidney doesnt let albumin pass from the blood into the urine.
It is helpful to divide the causes of intrinsic renal azotemia among categories that delineate the site of the initiating injury. GFR 50 normal BUN creatinine normal pt. The underlying pathology can be a guide for treatment and assessment of prognosis.
Renal fibrosis the final common pathway in the pathophysiology of DKD is caused by at least renal hemodynamic changes ischemia and glucose metabolism abnormalities-associated oxidative stress increases inflammatory processes and overactive renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system RAAS7 Fig. Acute kidney injury AKI is the clinical term used for decline or loss of renal function. The variability in the occurrence of AKI has been attributed to the difference in geographic locations raceethnicity and severity of illness.
Mechanisms of renal osteodystrophy. Loss of kidney function results in impaired H secretion from the body. Know the pathophysiology casues stages symptoms and diagnosis of chronic renal disease.
Initially kidney failure may cause no symptoms. Three general regions can be distinguished in each kidney. Lessons learnt from population databases are important.
4 stages I renal reserve. Damaged kidneys fail to excrete phosphate. Chronic renal failure is caused by a progressive decline in all kidney functions ending with terminal kidney damage.
When chronic kidney disease reaches an advanced stage dangerous levels of fluid electrolytes and wastes can build up in your body. GFR less than 20- 25 kidneys cannot regulate volume ions. Chronic renal failure.
Download high-res image 611KB. GFR 20-50 of normal azotemia anemia BP polyurianocturia via concentrating ability III renal failure. In the early stages of chronic kidney disease you may have few signs or.
The pathophysiology and treatment of obstructive uropathy are discussed extensively in another chapter. Nevertheless risk factors toward kidney stone development can be intrinsic such as age and sex or extrinsic such as diet and climate BAUS 2014. Protein-energy malnutrition due to metabolic acidosis.
Symptoms of kidney failure are due to the build-up of waste products and excess fluid in the body that may cause weakness shortness of breath lethargy swelling and confusion. The kidneys lie retroperitoneally on either sides of the vertebral columns at the level of T12 to L3Renal parenchyma comprises and outer cortex and inner medulla. Inability of the kidneys to secrete potassium in the urine leads to life threatening arrhythmias.
Intrinsic or Intra-Renal Acute Kidney Injury. During this time there is modulation and adaptation in the still-functional glomeruli which keeps the kidneys functioning normally for as long as possible. Arterial blood is supplied to kidneys via the renal arteries which branch off from abdominal aorta and.
The pathophysiology of kidney stones nephrolithiasis is not yet fully understood Bao and Wei 2012. It is associated with chronic kidney disease CKD and high morbidity and mortality. When the filters are damaged a protein called albumin which you need to stay healthy passes out of your blood and into your urine.
Data on the pathophysiology of kidney stone formation have been acquired via population-based epidemiology human metabolic studies and basic science experiments. However not all causes of AKI lead to severe consequences and some are reversible. The cortex is the outer layer of the kidney just deep into the renal capsuleThe medulla is consist is consist of several triangular renal pyramids and located deep into the cortex.
Acute kidney injury AKI is common among hospitalized patients with Coronavirus Infectious Disease 2019 COVID-19 with the occurrence of AKI ranging from 05 to 80.
 Overview Of Factors Contributing To The Pathophysiology Of Progressive Renal Disease Kidney International
Overview Of Factors Contributing To The Pathophysiology Of Progressive Renal Disease Kidney International
Chronic Kidney Disease Ckd Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review
 Management Of Acute Kidney Injury In Patients With Covid 19 The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Management Of Acute Kidney Injury In Patients With Covid 19 The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Chronic Kidney Disease Ckd Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review
 Cardiovascular Disease In Chronic Kidney Disease A Clinical Update From Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes Kdigo Kidney International
Cardiovascular Disease In Chronic Kidney Disease A Clinical Update From Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes Kdigo Kidney International
 Pathophysiology Of Renal Disease Image Chapter 26 Acute Renal Failure And Chronic Kidney Disease Renal Disease Acute Renal Failure Kidney Disease
Pathophysiology Of Renal Disease Image Chapter 26 Acute Renal Failure And Chronic Kidney Disease Renal Disease Acute Renal Failure Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease Ckd Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review
 Theoretical Schema For The Pathogenesis Of Chronic Kidney Disease Ecm Download Scientific Diagram
Theoretical Schema For The Pathogenesis Of Chronic Kidney Disease Ecm Download Scientific Diagram
 Pathogenesis Of Chronic Kidney Disease Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review Chronic Kidney Disease Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Nursing
Pathogenesis Of Chronic Kidney Disease Mcmaster Pathophysiology Review Chronic Kidney Disease Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Nursing
 Frontiers Renal Oxygenation In The Pathophysiology Of Chronic Kidney Disease Physiology
Frontiers Renal Oxygenation In The Pathophysiology Of Chronic Kidney Disease Physiology
Pre Renal Acute Kidney Injury Pathogenesis Calgary Guide
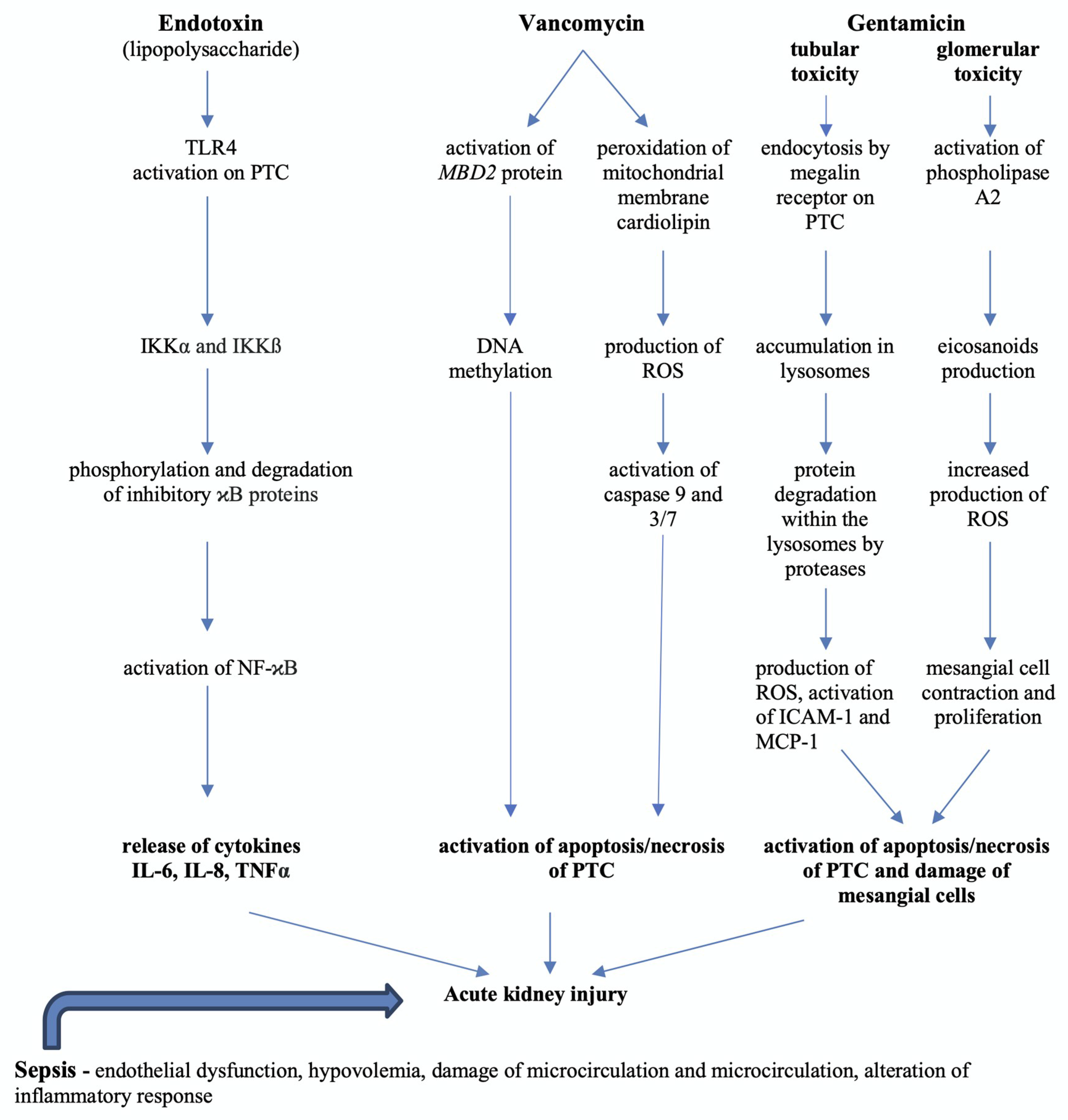 Ijms Free Full Text Acute Kidney Injury In Septic Patients Treated By Selected Nephrotoxic Antibiotic Agents Pathophysiology And Biomarkers A Review Html
Ijms Free Full Text Acute Kidney Injury In Septic Patients Treated By Selected Nephrotoxic Antibiotic Agents Pathophysiology And Biomarkers A Review Html
 Renal Disease Pathophysiology Of Disease An Introduction To Clinical Medicine Lange Medical Books 7th Ed
Renal Disease Pathophysiology Of Disease An Introduction To Clinical Medicine Lange Medical Books 7th Ed

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.